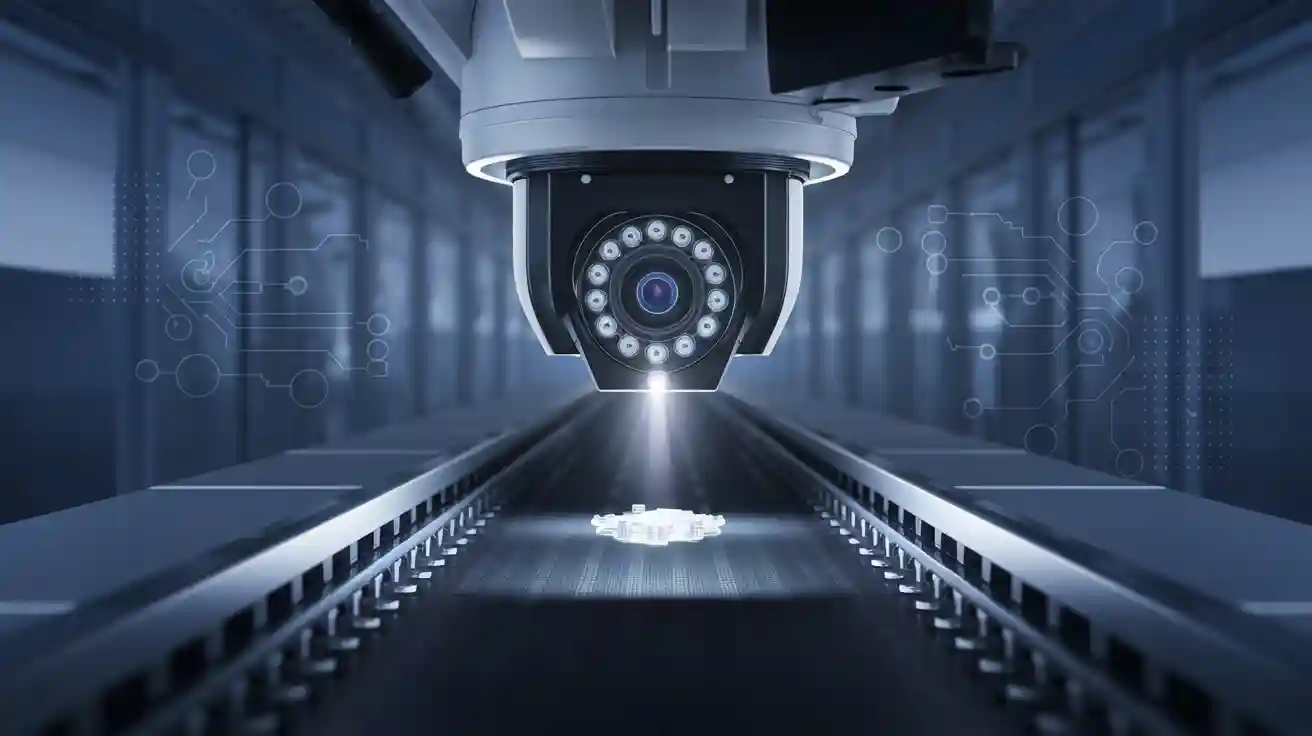
Imagine a factory where traditional light sources struggle to reveal tiny defects during inspection. A spot light machine vision system changes this scene. This system uses focused LED light to provide up to 300,000 lux, making even the smallest flaw visible. The importance of lighting becomes clear in the immediate inspection environment. LED spot lights offer stable, high-intensity light, which boosts inspection accuracy and reliability. Many industries now choose this system for its ability to adapt to different light conditions and improve results in every immediate inspection environment. The market for these systems continues to grow as manufacturers recognize their value in any immediate inspection environment.
Key Takeaways
- Spot light machine vision systems use focused LED light to reveal tiny defects that traditional lighting often misses, improving inspection accuracy.
- These systems adjust light angle, color, and intensity to match different products and environments, making inspections flexible and reliable.
- High-intensity, stable lighting helps capture clear images quickly, reducing errors and speeding up production lines.
- The system supports various lighting techniques like bright field and dark field to highlight different surface features and defects.
- Many industries benefit from these systems by lowering defect rates, cutting inspection costs, and boosting product quality and efficiency.
Spot Light Machine Vision System
How It Works
A spot light machine vision system uses advanced technology to help factories and industries see details that normal lights cannot show. The system has three main parts: the machine, the vision, and the system software. Each part plays a special role in making sure the inspection works well.
| Component Category | Core Components | Role/Function |
|---|---|---|
| Machine | Mechanical arms, conveyor belts, automated equipment | Moves and controls objects for inspection |
| Vision | Light sources (including spot lights), industrial lenses, industrial cameras, image acquisition cards | Provides illumination, focuses, captures images, and converts signals |
| System | Software for image processing and analysis, industrial control hosts | Analyzes images, identifies features, measures, and controls tasks |
The vision part uses spot lights to shine a strong, focused beam on the object. This light helps the camera see tiny features and defects. The system collects images by using different illumination techniques. Bright field lighting makes surface scratches and marks easy to see. Dark field lighting shows edges and small bumps. Diffuse lighting spreads the light evenly, which helps when the surface is shiny. Backlighting creates a silhouette, making it easier to measure shapes.
The system works in steps:
- The spot light shines on the object.
- The camera captures a clear image with high contrast.
- The software processes the image and finds important features.
- The system decides if the object passes or fails inspection.
Spot lights give the system high brightness and contrast. This makes it easier to find defects and measure objects. The system can adjust the light to match the inspection task. For example, it can change the color or angle of the light to highlight certain features. Some systems use adaptive lights that change brightness and color automatically. This helps the system work well in different environments.
Key Features
A spot light machine vision system offers many features that make it better than traditional lighting. The most important feature is the ability to use different illumination techniques. The system can switch between bright field, dark field, and diffuse lighting. This flexibility helps the system handle many types of inspections.
- Adjustable optics let the system change the focus and spread of the light. This means the system can work at different distances and with objects of different sizes.
- Integrated lights and smart drivers allow the system to use continuous, boosted, or strobe modes. These modes help control the intensity and timing of the light.
- Accessories like polarizing filters can be added to reduce glare and reflections. This makes the images clearer and more useful for inspection.
- The system supports multiple lens options. For example, some spot lights have beam angles of 26°, 32°, 61°, or 77°. This lets the system choose between focused or diffused light for each task.
Tip: Using the right illumination technique can make a big difference in image quality. For shiny surfaces, diffuse lighting works best. For finding small scratches, dark field lighting is the top choice.
The spot light machine vision system uses LED lights. These lights last a long time and use less power than old-style bulbs. They stay cool, so the system can run for hours without overheating. The system also works well in tough industrial settings because the lights are strong and reliable.
Machine vision lighting must create high contrast between the object and the background. This helps the camera see important details. The light must also be bright enough to reduce noise and keep the image sharp. The system needs to keep the light stable, even if the object moves or tilts. This ensures every image looks the same, making inspections more accurate.
The system can use different types of machine vision lighting, such as spot lights, ring lights, and backlights. Each type has its own job. Spot lights focus on small areas, while ring lights cover larger surfaces. Backlights help measure shapes and sizes.
Machine vision lighting in a spot light machine vision system gives factories the tools they need to inspect products quickly and accurately. The system adapts to many tasks by changing the light’s color, angle, and intensity. This makes it a smart choice for modern manufacturing.
Advantages
Precision
Spot light machine vision systems deliver outstanding precision in every inspection. The focused beam of light highlights even the smallest features on a product. This makes it possible to detect tiny scratches, cracks, or defects that other lighting methods might miss. The system uses different lighting techniques, such as bright field and dark field, to reveal specific details. For example, dark field lighting helps find small bumps or edges, while bright field lighting shows surface marks clearly.
The system can adjust the angle, color, and intensity of the light to match the inspection task. This flexibility ensures that the camera captures high-contrast images every time. Experts explain that matching the spectral output of the light to the camera sensor improves the ability to see fine details. The system software processes these images quickly, measuring and identifying features with high accuracy. In industrial settings, structured light patterns enable 3D imaging, allowing the system to measure depth and shape with errors under 1 cm within a 500 mm range. This level of precision helps reduce defects and improve product quality.
Note: The importance of lighting cannot be overstated. Proper light selection and control make the difference between a missed defect and a perfect inspection.
Reliability
Reliability stands at the core of spot light machine vision systems. These systems maintain consistent performance even in tough industrial environments. Several design features support this reliability:
- High-intensity, uniform illumination adapts to different working distances and imaging conditions.
- Embedded control features, such as overdrive strobe functionality, allow precise timing and intensity control. This reduces heat and improves image quality.
- Modular, field-swappable optics and components enable on-site adjustments to beam angle and light conditioning.
- Industrial-grade construction ensures durability and long-term reliability, even in demanding logistics settings.
- The system design reduces the number of fixtures needed, simplifying installation and lowering power consumption.
Experts in machine vision lighting point out that protecting LED lights from environmental hazards is key. Rugged enclosures rated by IP and NEMA standards shield the lights from moisture, dust, and chemicals. Washdown-rated lights add another layer of protection. Active cooling methods, such as fans or liquid cooling, keep the lights at safe temperatures. Strobing techniques only activate the lights during image capture, reducing heat buildup. Internal heating elements and closed-loop temperature monitoring prevent damage from cold or condensation. These combined features ensure the system delivers uniform illumination and reliable image capture, even with vibration, temperature swings, or exposure to harsh substances.
Manufacturers customize machine vision systems to handle complex product shapes, surfaces, and environments. They use glare-reducing lighting, polarizers, and dome lighting to ensure accurate inspection under difficult conditions. Modular fixtures and environment control enclosures isolate inspections from ambient disturbances. These engineering solutions enable reliable, repeatable inspection in continuous production, even for high-speed or variable products.
Flexibility
Spot light machine vision systems adapt easily to different inspection tasks and product types. The system considers the physical constraints of the inspection environment, such as limited access or the presence of robotic equipment. It manages ambient light using high-power strobing, enclosures, or filters to keep inspection quality high. The system optimizes lighting based on how the product surface interacts with light—taking into account shape, reflectivity, and texture. This approach maximizes contrast on features of interest and reduces unwanted reflections or glare.
The system software allows quick changes to inspection settings, enabling fast adaptation to new products or tasks. Physical constraints and ambient light conditions influence lighting choices and system setup, ensuring flexibility across varied inspection environments.
| Lighting Type | Adaptation Purpose / Benefit |
|---|---|
| Ring lights | Provide even illumination, reduce shadows; ideal for flat surfaces |
| Backlights | Illuminate from behind to highlight edges; useful for detecting cracks or missing parts |
| Bar lights | Side illumination to reveal surface defects like scratches or dents |
| Diffuse dome lights | Soft, spread light to reduce glare and reveal small defects on shiny surfaces |
Proper lighting reveals features to be inspected and suppresses irrelevant details. Stable, regulated lighting avoids false detections caused by light fluctuations. The system uses different lighting techniques, such as back lighting, off-axis lighting, dome lighting, spot lighting, and dark field lighting. Selecting the right technique depends on the part’s characteristics and inspection goals. This enables the system to adapt to diverse product types and inspection tasks.
Tip: Quick changes to lighting settings help factories switch between different products without slowing down production.
Machine Vision Applications

Surface Inspection
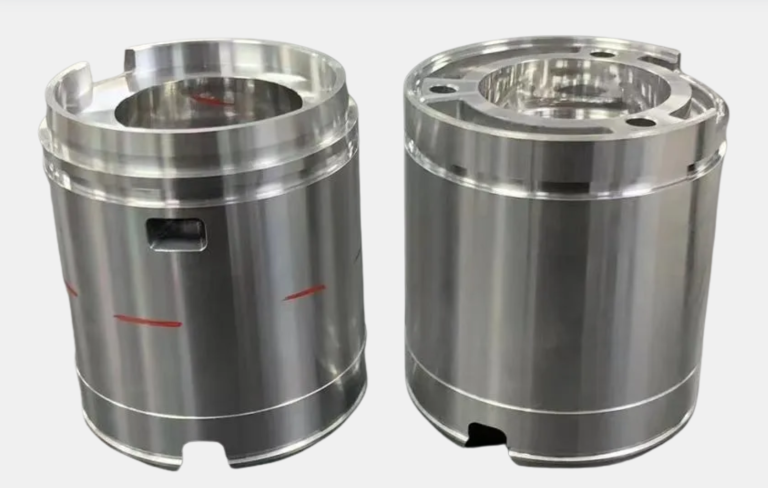
Surface inspection stands as one of the most common machine vision applications. Factories use spot light to reveal tiny scratches, dents, or marks on products. When traditional lighting creates glare or shadows, spot light provides focused and controlled illumination. This approach helps the camera capture clear images without noise. Research shows that non-uniform lighting can hide defects, but spot light overcomes this by shining directly on reflective or curved surfaces. The right amount of light, often above 1000 lux, makes small defects visible. High-intensity spot light ensures both human inspectors and automated systems can see every detail. In electronics, spot light helps find flaws on circuit boards. In packaging, it checks for surface damage on boxes and bottles. By improving image quality, spot light reduces false rejects and increases inspection accuracy.
Dimensional Measurement
Dimensional measurement is another important use of machine vision applications. Manufacturers need to measure parts without touching them. Spot light, combined with high-resolution cameras, allows for non-contact measurement. In the automotive industry, vision systems use spot light to check engine blocks, car seats, and assembly parts. For example, a robot-guided system with Z-SPOT spot light inspects mounting holes in car seats. This system uses powerful light to reach tight spaces and ensure thread quality. Electronics factories use spot light to measure thin or fragile parts. The light highlights edges and shapes, making it easy for software to calculate dimensions. These systems work quickly, making them ideal for high-speed production lines. AI and user-friendly software improve the process, helping factories keep up with demand.
Defect Detection
Defect detection benefits greatly from spot light in machine vision applications. Spot light creates shadows and contrast that reveal cracks, scratches, and edges. Uniform diffuse lighting can hide these defects, but spot light makes them stand out. Studies show that directional lighting, like dark-field or angled light, increases detection rates. For example, detection of shallow scratches can reach up to 82% with the right light. Combining spot light with shadowless lighting balances defect visibility and reduces false alarms. In packaging and logistics, spot light helps robots pick items of any shape or size. 3D vision systems use spot light to sort packages, detect obstacles, and guide automated vehicles. These systems improve safety and reduce errors in warehouses. The use of spot light in machine vision applications leads to more reliable inspections and better product quality.
Tip: Choosing the right light for each inspection task can boost detection rates and reduce missed defects.
Choosing Machine Vision Lighting
Selection Tips
Choosing the right machine vision lighting starts with understanding the inspection environment. Engineers look at the space, the amount of ambient light, and how samples move through the area. They study the surface of each item, checking for reflectivity, color, and texture. The type of light matters. LED lights work well for most tasks because they last long and give stable output. Some jobs need more intense light, so engineers pick lights that can reach over 60,000 Lux at a 300mm working distance. Matching the color of the light to the camera sensor helps the system see details better. The four main points for good lighting setup are geometry, pattern, wavelength, and filters. These help create strong contrast where it matters most. Engineers also make sure the lighting setup can handle changes in part size, shape, and placement. They use high-power strobing or filters to block out unwanted ambient light. Safety and speed matter too, so they pick lights that fit the workspace and keep workers safe.
Tip: Always test the lighting setup early in the design process. Early testing helps avoid problems and saves time.
Integration
Integrating machine vision lighting into a production line takes careful planning. Teams start by listing what the system needs to do. They treat lighting as a key part of the project. Early installation and offline testing of the light and camera help find problems before production starts. A good plan for validation checks that the system works every time. Lighting setup design uses the best techniques to get clear images. Many teams use experts in both engineering and lighting to make sure the system fits well. Lighting makes up about 80% of machine vision system performance, so it gets special attention. Advances in software now make it easier to add lighting to existing lines. Teams also protect the system from dust, vibration, and temperature swings. They use covers to keep dust off the camera and lights. Shockproof mounts stop vibration from blurring images. Temperature controls keep the system working in hot or cold areas.
Optimization
Lighting optimization means getting the best results from the system. Bright light helps find missing material by showing texture differences. Picking the right color of light, like blue for certain chips, makes features stand out. Non-diffused light, such as dark field lighting, shows cracks in clear materials. Diffuse lighting removes reflections when checking clear packaging. Color lighting can help the system see differences between features and the background. Strobe lighting freezes moving parts, stopping blur. Infrared light removes unwanted reflections and makes images more even. Regular calibration keeps the system accurate. Teams use special algorithms to improve how the system makes decisions in real time. They also plan for changes in ambient light, shadows, and reflections. Early design choices for lighting setup help avoid costly mistakes. Testing different lighting choices helps find the best setup for each job.
| Factor | Effect on Performance | Example / Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Working Distance | Affects coverage and brightness; longer distances need higher intensity to keep light strong and even. | 65mm coverage at 300mm; up to 2700mm with high-intensity light (up to 110,000 Lux). |
| Intensity | Needed for clear images; adjustable intensity lets teams match light to each inspection task. | Manual controls and controllers allow 0-100% intensity changes. |
| Lens Options | Change how light spreads and focuses; special lenses create bright, even spots for all distances. | Molded TIR and telecentric lenses help with different machine vision lighting needs. |
Note: Lighting setup should always match the inspection task. The right light, angle, and color make a big difference in image quality.
Success Stories
Case Study
A leading automotive supplier faced challenges with traditional inspection methods. The company needed to detect wrinkles and defects in car seat covers. The team installed a spot light machine vision system. The system used high-intensity light to focus on every detail. The light revealed wrinkles that older systems missed. The inspection process improved. The company saw a 99% accuracy rate in defect detection. The defect rate dropped by 30%. Inspection time fell from 1 minute to just 2.2 seconds per seat. The system integrated seamlessly into the production line. Automated wrinkle correction used a six-axis robot guided by the light. The company reduced inspection costs by a factor of 30. Full return on investment came in under two years.
| Metric | Result / Improvement |
|---|---|
| Accuracy of defect detection | 99% accuracy in wrinkle defect detection |
| Defect rate reduction | 30% reduction in defect rates |
| Inspection time | Reduced from 1 minute to 2.2 seconds per seat |
| Cost savings | Inspection costs reduced by a factor of 30 |
| ROI | Full return on investment in under 2 years |
| Integration | Seamless integration into existing production line |
| Additional benefit | Automated wrinkle correction via six-axis robot |
Testimonial
Schneider Electric adopted a spot light machine vision system for packaging inspection. The team used Cognex vision and AI-based solutions. The light handled variability in recycled material packaging. Automated inspections reduced false rejects. The process drift decreased. Product quality improved. The system increased production speed and efficiency. The light reduced scrap, raw material use, and energy. Closed-loop feedback optimized manufacturing in real time. The partnership continues to enhance quality control and reduce waste.
- Schneider Electric used Cognex machine vision and AI-based solutions to handle variability in recycled material packaging inspection.
- Automated inspections reduced false rejects and mitigated process drift, maintaining product quality.
- Increased production speed and efficiency through augmented or fully automated inspection lines.
- Improved sustainability by reducing scrap, raw material consumption, and energy usage.
- Enabled closed-loop feedback systems to optimize manufacturing parameters in real-time.
- Long-term partnership aims to further enhance quality control, reduce waste, and improve supply chain efficiency.
Results
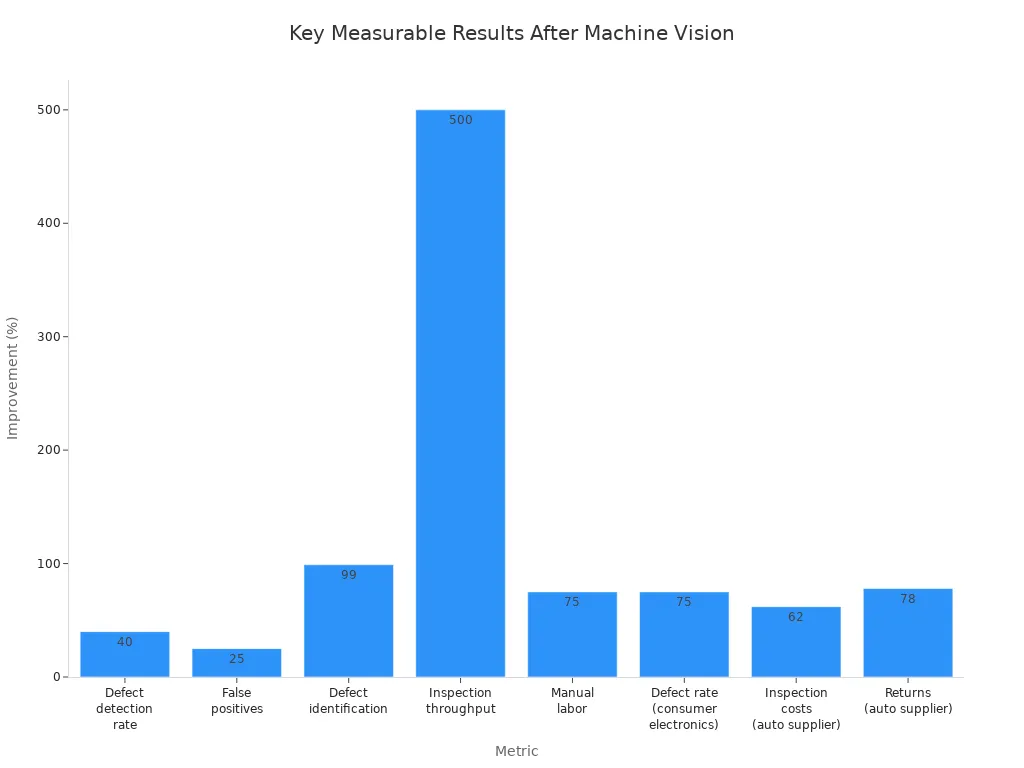
Spot light machine vision systems deliver measurable improvements. The light increases defect detection rates by over 40%. False positives drop by up to 25%. The system achieves over 99% accuracy in defect identification. Inspection throughput rises sixfold. Manual labor drops to one quarter. In consumer electronics, the defect rate falls by 75%. Automotive suppliers see inspection costs drop by 62% and returns by 78%. Inspection speed improves from 2-3 seconds per unit to 0.2 seconds per unit. The light enables scalability, handling ten times more volume than before.
Industry professionals report that spot light machine vision systems provide long-term benefits. The light automates inspections with high speed and accuracy. The system reduces human error and improves product quality. Consistent and objective evaluations outperform manual inspections. The light supports high-speed production lines and reduces costs from defects and rework. The system enables traceability and data analytics, supporting Industry 4.0 goals. Lighting experts highlight durability, low maintenance, and design flexibility. The light adapts to diverse applications and ensures consistent image quality. The system faces challenges in scaling and integration, but advanced lighting remains critical for performance and cost-effectiveness.
Spot light machine vision systems transform inspection by using advanced light to reveal even the smallest defects. Many industries now rely on this light for automation, quality control, and efficiency. The light replaces manual checks, reduces errors, and ensures every inspection meets high standards. Companies see fewer defects, less waste, and better product quality because of this light. The market for this light grows as more sectors adopt it. Manufacturers should review their inspection steps, look for areas where light can improve results, and consider phased upgrades. Experts and providers offer guidance on choosing the right light and system for each inspection. The future brings even smarter light, with AI and new imaging making inspection faster and more accurate. For any business, the right light means better inspection and lasting success.
FAQ
What makes spot light machine vision systems better than traditional lighting?
Spot light machine vision systems use focused light to reveal small defects. The light creates high contrast and clear images. Traditional lighting often misses tiny flaws. The system adjusts the light for each inspection. This flexibility helps factories find problems early and improve product quality.
How does the system control the intensity and direction of the light?
The system uses adjustable optics and smart drivers. These parts change the light’s angle and brightness. Operators can set the light to match each task. The light can shine from different directions. This control helps the camera capture the best image for inspection.
Can spot light machine vision systems work in harsh environments?
Yes, these systems use strong light sources and rugged enclosures. The light stays stable even with dust, moisture, or vibration. The system uses cooling and protection features. This keeps the light working in tough places like factories or warehouses. The light ensures reliable inspection every time.
Why is the color of the light important in machine vision?
The color of the light affects how the camera sees details. Some colors make features stand out more. The system matches the light color to the camera sensor. This helps the light show small marks or defects. Using the right color of light improves inspection accuracy.
How do spot light systems handle different product shapes and surfaces?
The system changes the light’s angle, color, and intensity for each product. The light adapts to shiny, rough, or curved surfaces. The software sets the best light settings. This way, the light always shows the features that matter. The light helps inspect many types of products.
See Also
The Role Of Structured Light In Improving Vision Systems
Understanding The Basics Of Illumination In Vision Systems
Why Proper Lighting Equipment Is Vital For Vision Systems
An In-Depth Look At Cameras Used In Vision Systems
Exploring The Electronics Behind Machine Vision Systems Today








