Synthetic Data for Training AI Inspection Models plays a crucial role in enhancing machine vision systems. This type of data is artificially generated rather than sourced from real-world environments, making it an effective solution for addressing challenges such as limited access to diverse or high-quality datasets. By simulating a variety of conditions, synthetic data significantly improves AI training and boosts machine learning performance.
Synthetic Data for Training AI Inspection Models is particularly valuable in applications like defect detection and quality assurance. It enables machine vision systems to identify flaws, even in rare or complex scenarios, by exposing them to an extensive range of simulated situations. Leveraging synthetic data allows for the creation of smarter, more efficient AI inspection models tailored to meet specific requirements.
Key Takeaways
-
Synthetic data helps train AI by offering varied, good-quality datasets. It solves problems like lack of data and privacy issues.
-
Using synthetic data makes AI models more accurate and stronger. It helps AI learn from rare or tricky situations that real data might miss.
-
Adding synthetic data can cut costs and save time. This helps AI solutions reach the market faster.
-
Mixing synthetic and real data uses the best of both. This makes sure models are ready for real-world problems.
-
Checking synthetic datasets often is important to keep them good. This avoids mistakes and ensures AI works well.
Why Synthetic Data is Essential for AI Inspection Models
Solving Data Scarcity Challenges
You often face challenges when collecting high-quality training data for machine learning models. In many industries, such as healthcare and manufacturing, data is either incomplete, biased, or unbalanced. This makes it difficult to train AI systems effectively. Synthetic data offers a solution by generating datasets that are both diverse and privacy-compliant.
Did you know? Despite the vast amount of data generated daily, much of it is noisy and unstructured, limiting its usefulness for AI training. Synthetic data fills this gap by creating structured, high-quality datasets tailored to your needs.
Synthetic data also addresses privacy concerns. For example, in fields like finance, where sensitive information is involved, synthetic datasets can simulate real-world scenarios without exposing confidential details. This innovation accelerates AI research and ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
Improving Model Accuracy and Robustness
Synthetic data enhances the accuracy and robustness of machine learning models by providing a virtually unlimited supply of tailored training data. For instance, you can simulate rare defects in manufacturing processes or anomalies in industrial operations. This allows your AI systems to learn from scenarios they might not encounter in real-world data.
By using synthetic data, you can also reduce biases in your training data. This ensures that your AI models perform fairly across different conditions. For example, a fraud detection model can use synthetic transaction data to simulate both normal and fraudulent activities. Testing on these datasets helps identify weaknesses in detection capabilities, improving accuracy over time.
-
Synthetic data enables faster adaptation to data drift, ensuring your models remain effective as conditions change.
-
It allows you to retrain models using a mix of synthetic and real data, enhancing predictive power.
-
Studies show that synthetic data can improve model accuracy metrics, such as the mean Average Precision (mAP50) score, by up to 1.5%.
Reducing Costs and Accelerating Development
Traditional data collection methods are often expensive and time-consuming. Synthetic data significantly reduces these costs while speeding up the development process. For example, creating synthetic datasets eliminates the need for manual data labeling and extensive field testing.
|
Metric |
Synthetic Data Use |
Traditional Data Collection |
|---|---|---|
|
Average reduction in time-to-market |
35% |
N/A |
|
Average cost reduction in data acquisition |
47% |
N/A |
By leveraging synthetic data, you can bring AI solutions to market faster and at a lower cost. This is especially beneficial for industries where rapid innovation is critical. Synthetic data also allows you to test and refine your models in a controlled environment, reducing the risk of errors during deployment.
Tip: Incorporating synthetic data into your AI training pipeline not only saves time and money but also ensures that your models are better prepared for real-world challenges.
Types of Synthetic Data for Training AI Inspection Models Machine Vision System
Procedural Generation
Procedural generation uses algorithms to create synthetic data automatically. This method allows you to generate synthetic data with high scalability and variety. For example, you can create thousands of unique images of defective products by adjusting parameters like shape, color, and texture. Studies, such as those by Nikolenko, show that procedural generation can outperform real-world data in scalability. It also reduces the time and cost of data collection.
In industries like automotive manufacturing, procedural modeling combined with physically based rendering has proven effective. Research by Tsirikoglou et al. highlights how this approach helps train AI systems for autonomous vehicles. You can simulate diverse driving conditions, such as rain or fog, without needing to collect real-world data. This makes procedural generation a powerful tool for creating ai-generated synthetic data tailored to specific needs.
Tip: Use procedural generation to simulate rare or dangerous scenarios that are difficult to capture in real life.
Simulation-Based Data
Simulation-based data relies on virtual environments to mimic real-world conditions. This method is particularly useful when you need to train AI models for tasks like image segmentation or object detection. Simulations allow you to control every aspect of the environment, ensuring consistency and precision.
Empirical studies reveal that simulation-based data significantly enhances model accuracy, especially when real-world data is scarce. For instance, you can simulate industrial operations to train AI systems for defect detection. These simulations not only improve performance but also reduce biases that often exist in limited datasets. By using this approach, you can generate synthetic data that mirrors real-world complexities while maintaining high quality.
Augmented Data from Real-World Sources
Augmentation involves enhancing real-world data to create new, synthetic variations. Techniques like rotation, scaling, and color adjustments help you expand your dataset without collecting additional samples. This method, known as data augmentation, is particularly effective for improving model robustness.
For example, you can take images of manufactured products and apply transformations to simulate different lighting conditions or angles. This process generates ai-generated synthetic data that enriches your training set. Augmented data bridges the gap between real and synthetic data, offering a cost-effective way to improve AI performance.
Did you know? Augmented data accounts for a significant portion of ai-generated synthetic data, alongside structured and unstructured synthetic datasets.
Comparing Synthetic Data and Real Data
Key Advantages of Synthetic Data
Synthetic data offers several advantages that make it a powerful tool for training AI inspection models. One of its most significant benefits is enhanced data privacy. By generating artificial datasets, you can reduce privacy risks and ensure compliance with regulations, especially in industries like healthcare and finance. Synthetic data also stands out for its cost-effectiveness. Unlike real data, which often requires expensive collection and labeling processes, synthetic datasets can be created efficiently, saving both time and money.
Another key advantage is scalability. Synthetic data allows you to quickly produce extensive datasets to meet your training and testing requirements. This is particularly useful when dealing with rare or complex scenarios that are difficult to capture in real-world environments. Additionally, synthetic data enables controlled experimentation. You can manipulate variables to create specific scenarios, ensuring your AI models are robust and well-prepared for diverse challenges.
|
Advantage |
Synthetic Data |
Real Data |
|---|---|---|
|
Data Privacy |
Significantly reduces privacy risks |
Subject to privacy regulations |
|
Cost-Effectiveness |
Efficient generation leads to savings |
Often expensive to collect |
|
Scalability |
Quickly produces extensive datasets |
Limited by collection capabilities |
|
Controlled Experimentation |
Allows manipulation for specific scenarios |
Less flexibility in experimentation |
Tip: Use synthetic data to simulate rare events or edge cases that are hard to replicate in real-world conditions.
Limitations and Challenges of Synthetic Data
While synthetic data offers many benefits, it also comes with limitations. One major challenge is the lack of realism and accuracy. Synthetic datasets often fail to capture the subtle nuances of real-world data, which can lead to inaccuracies in AI model predictions. Generating complex data, such as realistic images or natural language text, is another hurdle. This process requires advanced techniques and significant computational resources.
Validating synthetic data poses additional difficulties. Ensuring that these datasets accurately reflect real-world trends is crucial for maintaining model reliability. Synthetic data also depends heavily on the quality of the underlying real-world data. If the original data contains errors or biases, these issues can carry over into the synthetic datasets, potentially leading to unfair outcomes or flawed predictions.
-
Lack of realism and accuracy can affect model performance.
-
Generating complex data requires sophisticated techniques.
-
Validation challenges make it hard to ensure data quality.
-
Dependency on real data introduces risks if the original data is flawed.
-
Biases in real-world data can propagate into synthetic datasets.
Note: Always evaluate the quality of your synthetic data to ensure it aligns with your AI model’s requirements.
Choosing Between Synthetic and Real Data
Deciding whether to use synthetic or real data depends on your specific needs and goals. Synthetic data is ideal for testing rare events or scenarios that are difficult to capture in real life. For example, you can use it to simulate defects in manufacturing processes or anomalies in industrial operations. This approach enhances the robustness of your AI models and prepares them for unexpected challenges.
On the other hand, real data is crucial for evaluating real-world performance. Production replay logs, which reflect actual user interactions, provide valuable insights into how your AI systems perform in practical applications. When choosing between synthetic and real data, consider success metrics that align with your business objectives. These metrics may include technical measures like precision and recall, as well as business KPIs such as cost savings and customer retention.
-
Synthetic data is best for testing rare or complex scenarios.
-
Real data is essential for assessing real-world performance.
-
Align your success metrics with both technical and business goals.
Tip: Combine synthetic and real data to leverage the strengths of both and achieve optimal results for your AI inspection models.
Applications of Synthetic Data in AI Inspection Models
Defect Detection in Manufacturing Processes
Synthetic data plays a transformative role in defect detection within manufacturing. By simulating various defect scenarios, you can train AI models to identify flaws that might otherwise go unnoticed. This approach ensures your models are prepared for rare or complex defects, improving their overall performance. For example, synthetic data allows you to replicate scratches, dents, or misalignments on products, enabling your AI systems to detect these issues with greater accuracy.
To validate the effectiveness of synthetic data in defect detection, several metrics are used:
|
Metric Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Fidelity Assessment |
Ensures synthetic data accurately reflects real data characteristics to maintain model performance. |
|
Statistical Tests |
Methods like Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Anderson-Darling compare distributions of synthetic and real data. |
|
Performance Metrics |
Metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, and ROC-AUC score evaluate model effectiveness. |
|
Similarity Metrics |
Compare distributions of synthetic and original data using metrics like mean squared error. |
|
Classification Accuracy |
Validates utility by training on original data and testing on synthetic data for similar accuracy. |
Defect detection rates improve significantly when synthetic data is used. Studies show an average increase of 32% in detection rates, especially when augmented analytics are applied in quality control processes.
Quality Assurance in Automated Systems
Synthetic data enhances quality assurance by enabling automated systems to perform consistent and accurate checks. You can use synthetic datasets to simulate diverse scenarios, ensuring your models remain robust under varying conditions. This approach reduces errors and improves the consistency of quality checks.
Key strategies for leveraging synthetic data in quality assurance include:
|
Strategy |
Benefits |
Implementation Rate |
|---|---|---|
|
Automated Quality Checks |
Reduced errors, Improved consistency |
85% |
|
Multiple Data Sources |
Enhanced diversity, Better representation |
72% |
|
Regular Dataset Reviews |
Maintained relevance, Updated insights |
68% |
|
Model Audit Processes |
Improved accuracy, Reduced bias |
59% |
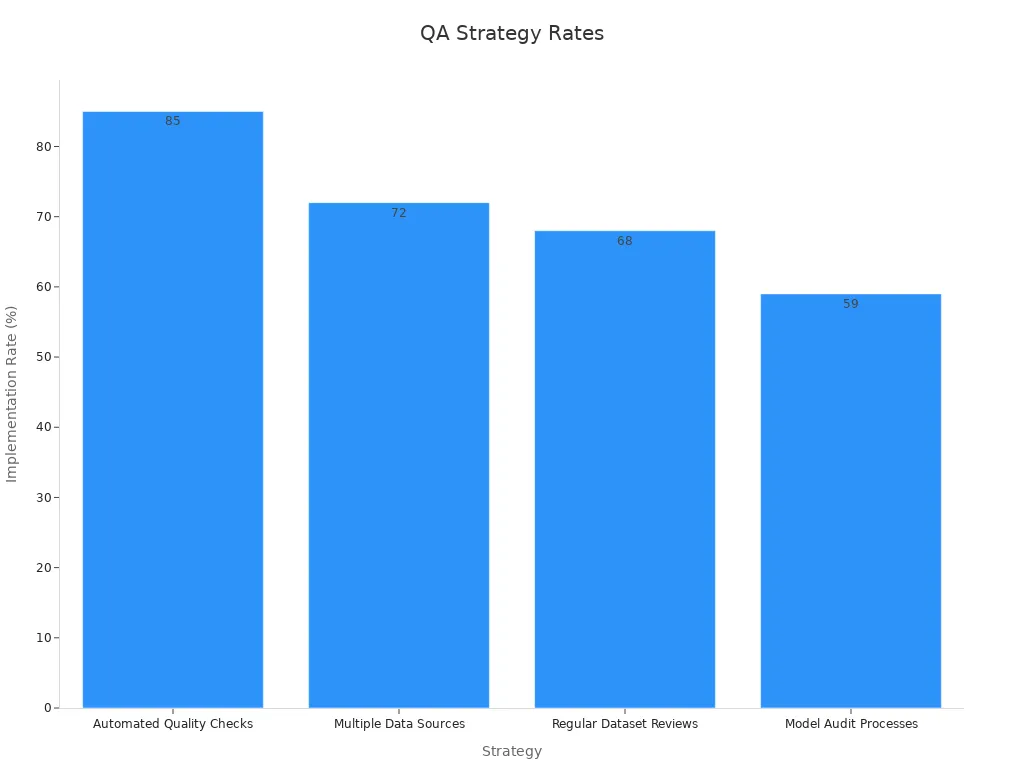
By adopting these strategies, you can ensure your AI systems deliver reliable results while minimizing the risk of bias or outdated insights.
Anomaly Detection in Industrial Operations
In industrial operations, detecting anomalies is critical for maintaining efficiency and safety. Synthetic data provides a controlled environment for training AI models to recognize unusual patterns or behaviors. For instance, you can use Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to create synthetic datasets that mimic real-world anomalies.
Research shows that using GANs improves anomaly detection rates by 9.93% in terms of the Area Under the Curve (AUC). This improvement was observed across twelve public datasets, highlighting the effectiveness of synthetic data in enhancing detection capabilities.
Synthetic data also allows you to test your models against a wide range of scenarios, ensuring they perform well under different conditions. This flexibility makes it an invaluable tool for anomaly detection in industries like energy, logistics, and manufacturing.
Risks and Ethical Considerations of Synthetic Data
Addressing Bias in Synthetic Data
Bias in synthetic data can lead to inaccurate predictions and unfair outcomes in AI systems. Discrepancies between synthetic and real-world datasets often create data distribution bias. This can mislead machine learning models, especially in tasks like defect detection or quality assurance. For example, if synthetic data lacks diversity, your AI system may fail to generalize across different scenarios.
To address this, you should implement bias detection and mitigation protocols. Comparing the statistical properties of synthetic data with real-world data helps identify inconsistencies. Additionally, using domain-specific metrics ensures the data reflects real-world conditions accurately. Regular validation and auditing of synthetic datasets are essential steps to maintain fairness and reliability.
Tip: Always review your synthetic datasets to ensure they capture the diversity and complexity of real-world situations.
Avoiding Overfitting to Unrealistic Scenarios
Overfitting occurs when AI models perform well on training data but fail in real-world applications. Synthetic data, if not carefully designed, can exacerbate this issue by introducing unrealistic scenarios. For instance, overly simplistic or exaggerated synthetic datasets may cause your model to learn patterns that do not exist in real-world environments.
You can prevent overfitting by focusing on data quality and representativeness. Techniques like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) enhance the realism of synthetic data. Conducting thorough validation ensures your datasets align with real-world trends. Additionally, combining synthetic data with real-world data improves model generalization and reduces the risk of overfitting.
Note: Diverse and high-quality synthetic data is key to building robust machine learning models.
Ethical Implications of Artificial Data Generation
The creation of synthetic data raises several ethical concerns. Fictional scenarios, if misused, can spread misinformation or create unrealistic expectations. For example, synthetic datasets used in sensitive industries like healthcare or finance must adhere to strict ethical standards to avoid harm.
Ethical AI development requires you to follow principles like responsibility, fairness, and transparency. Ensuring privacy and preventing re-identification of individuals in synthetic datasets is critical. Additionally, explicability is vital. You should make AI systems transparent and accountable to build trust among users. By adhering to these principles, you can mitigate risks and promote ethical practices in artificial data generation.
Did you know? Ethical frameworks emphasize justice and autonomy, ensuring AI benefits are distributed fairly across all stakeholders.
Future of Synthetic Data for AI Inspection Models in 2025
Innovations in Simulation and Data Generation
Advancements in synthetic data generation are transforming how you train AI inspection models. Techniques like procedural generation, simulation engines, and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are leading the way. These methods allow you to create highly realistic and diverse datasets tailored to specific needs.
|
Technique |
Advantages |
Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
|
Procedural Generation |
Highly customizable, scalable, and efficient |
Simulating various lighting conditions, object orientations, and environmental factors. |
|
Simulation Engines |
High realism, interactive simulations |
Training autonomous vehicle perception systems, virtual reality applications, and robotics. |
|
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) |
Ability to generate highly realistic and diverse data |
Creating synthetic images for training, data augmentation, and filling gaps in real datasets. |
These innovations improve efficiency and reduce costs. For example, GANs can generate synthetic images that mimic real-world conditions, enhancing model accuracy. By 2030, synthetic data is expected to dominate AI training, addressing challenges like data scarcity and bias.
Real-Time Integration with Machine Vision Systems
Real-time integration of synthetic data with machine vision systems is becoming a reality. This allows you to train and deploy AI models faster. Synthetic data can simulate real-time scenarios, enabling your systems to adapt to changing conditions. For instance, in manufacturing, you can use synthetic datasets to monitor production lines and detect defects instantly.
This integration also enhances predictive maintenance. By simulating potential equipment failures, you can train AI systems to identify issues before they occur. This reduces downtime and improves operational efficiency.
Expanding Adoption Across Industries
Synthetic data is gaining traction across various sectors. Industries like healthcare, automotive, and finance are leading the adoption. By 2025, the adoption rate in healthcare is projected to reach 50%, while the automotive sector is expected to hit 70%. These industries benefit from synthetic data’s ability to enhance privacy, reduce costs, and improve model performance.
|
Industry |
Adoption Rate by 2025 |
Impact on Operations |
|---|---|---|
|
Healthcare |
50% |
Enhanced disease prediction models |
|
Automotive |
70% |
Accelerated ADAS development |
|
Finance |
65% |
Better fraud detection systems |
|
Retail |
30% |
Improved personalization |
|
Manufacturing |
58% |
Efficient quality control |
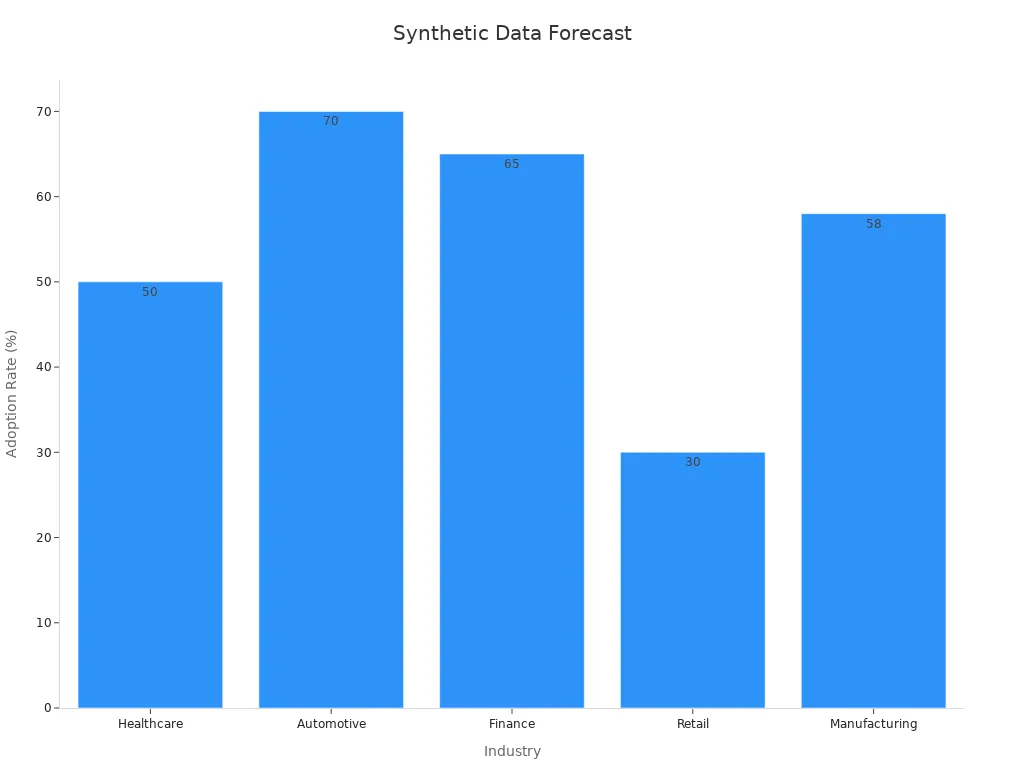
The synthetic data market is projected to grow from USD 300 million in 2024 to USD 13.0 billion by 2034, reflecting a remarkable CAGR of 45.9%. This growth highlights the increasing reliance on synthetic data to drive innovation and efficiency.
Synthetic data for training AI inspection models machine vision system has become a cornerstone of modern AI development. It addresses critical challenges like data scarcity and privacy concerns while offering unmatched scalability and cost-efficiency. By leveraging synthetic data, you can train models to detect defects, ensure quality, and identify anomalies with greater precision. For example, metrics like F1 scores and AUC values consistently range between 0.8 and 0.99, proving the reliability of synthetic datasets. Visual inspections also confirm that synthetic images closely resemble real-world data, ensuring robust model performance.
The benefits of synthetic data extend beyond accuracy. It accelerates development timelines, reduces costs, and enables you to simulate rare or complex scenarios. By 2025, advancements in simulation engines and real-time integration will further enhance its adoption across industries. As synthetic data continues to evolve, it will redefine how you train AI inspection models, ensuring smarter and more efficient machine vision systems.
FAQ
What is synthetic data, and how does it differ from real data?
Synthetic data is artificially generated information used to train AI models. Unlike real data, which comes from actual environments, synthetic data is created through algorithms or simulations. It mimics real-world scenarios while offering advantages like privacy, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Can synthetic data completely replace real data?
No, synthetic data complements real data but cannot fully replace it. Real data remains essential for validating AI models and ensuring real-world performance. Combining both types provides the best results, leveraging synthetic data’s scalability and real data’s authenticity.
How do you ensure synthetic data is realistic?
You ensure realism by using advanced techniques like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and simulation engines. These methods replicate real-world conditions with high accuracy. Regular validation against real data ensures synthetic datasets align with actual trends and scenarios.
Is synthetic data safe to use in sensitive industries?
Yes, synthetic data is safe for sensitive industries like healthcare and finance. It eliminates privacy risks by not containing real personal information. This makes it compliant with data protection regulations while still enabling effective AI training.
What are the main challenges of using synthetic data?
The main challenges include ensuring realism, avoiding overfitting, and addressing biases. Synthetic data must accurately reflect real-world conditions to prevent inaccuracies. Regular validation and combining it with real data help overcome these challenges.
See Also
Harnessing Synthetic Data To Enhance Machine Vision Capabilities
Synthetic Data Opens Doors To Innovative Machine Vision Solutions
Optimizing Visual Inspection Processes Using AI Technologies
Understanding Edge AI’s Role In Future Machine Vision Applications
The Impact of Generative AI On Tomorrow’s Manufacturing Landscape