Industrial cameras form the backbone of every industrial cameras machine vision system. These systems drive machine vision in factories, using advanced cameras for inspection and quality control. Many industrial cameras machine vision system types exist, including machine vision cameras, embedded vision cameras, and smart cameras. Each camera helps machine vision systems complete real-time inspections and monitor production. The table below shows some common camera types and their uses in machine vision:
| Camera Type | Key Features & Applications |
|---|---|
| Machine Vision Cameras | High-speed inspections, rugged design, large data handling |
| Embedded Vision Cameras | On-device processing, compact, real-time analysis |
| Global Shutter Cameras | No distortion for moving objects, used on assembly lines |
| Line Scan Cameras | Continuous inspection, wide material coverage |
| Thermal Cameras | Non-contact temperature checks, process monitoring |
| Hyperspectral Cameras | Detailed analysis, material sorting, complex inspection |
Key Takeaways
- Industrial cameras act as the eyes of machine vision systems, capturing images to inspect, measure, and sort products quickly and accurately.
- Different camera types like area scan, line scan, 3D, and smart cameras serve specific industrial tasks, improving quality control and automation.
- Advanced sensors, high frame rates, and smart processing enable cameras to handle fast-moving objects and complex inspections in real time.
- Proper lighting and optics are essential to capture clear images, which helps detect defects and measure products precisely.
- Machine vision systems with industrial cameras boost production speed, reduce errors and waste, and lower costs across many industries.
Industrial Cameras in Machine Vision Systems
Core Functions
Industrial cameras play a central role in machine vision systems. These cameras help machines see and understand their environment. They capture images of products and parts as they move through production lines. The images allow machine vision systems to make fast and accurate decisions.
Industrial cameras machine vision system setups perform several important tasks:
- Positioning: The cameras find the exact location of objects. This helps robots and machines pick up, move, or assemble parts with precision.
- Defect Detection: The cameras spot scratches, dust, or other defects on surfaces. This ensures only high-quality products leave the factory.
- Measurement: The cameras measure the size and shape of products. This allows for quick checks without touching the items.
- Identification: The cameras read barcodes and labels. This supports traceability and helps track products through the supply chain.
- Sorting: The cameras help sort products based on size, color, or type. This speeds up production and reduces errors.
Note: Industrial cameras act as the eyes of machine vision systems. They collect data that supports quality control, safety, and process improvement.
The table below shows how different camera systems support these core functions:
| Camera Type | Main Function(s) |
|---|---|
| Line Scan Camera | Inspects continuous materials, reads barcodes, monitors conveyor systems |
| Area Scan Camera | Detects defects, identifies parts, checks quality, inspects surfaces |
| 3D Scan Camera | Measures depth, guides robots, supports advanced inspection and smart manufacturing |
Machine vision cameras provide fast, reliable, and repeatable results. They reduce human error and improve production quality. Automated inspection with these cameras is faster and more accurate than manual checks. This leads to less waste and lower costs for manufacturers.
Key Technologies
Modern machine vision systems rely on advanced technologies to achieve high performance. The heart of every industrial cameras machine vision system is the sensor. Two main sensor types are used: CCD and CMOS. CMOS sensors allow higher frame rates, which means they can capture fast-moving objects. CCD sensors offer better image quality in low light but work more slowly. Most machine vision cameras today use CMOS sensors because they are faster, use less power, and cost less to make.
| Performance Aspect | CCD Sensors | CMOS Sensors |
|---|---|---|
| Image Quality | High, especially in low light | Improving with new technology |
| Speed | Slower | Faster, supports high frame rates |
| Power Use | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | More expensive | Cheaper |
Other important features in camera systems include:
- High frame rates: Capture images quickly, even when objects move fast.
- Global shutter: Prevents image distortion by capturing the whole image at once.
- High resolution: Finds tiny defects and measures small parts with accuracy.
- Low-light performance: Keeps images clear even in dim conditions.
- Durability: Works well in tough industrial environments.
Recent advances in machine vision include the use of AI and machine learning. These technologies help cameras recognize patterns, learn from data, and make decisions in real time. Some camera systems now have built-in processors, like GPUs or FPGAs, that allow for edge data analysis and industrial image processing. This means the camera can process images and make decisions without sending data to a separate computer.
3D imaging is another key technology. It allows machine vision systems to measure depth and shape, not just color and brightness. This helps robots pick up objects, check for missing parts, and inspect complex surfaces.
Tip: Choosing the right lens and lighting is just as important as picking the right camera. Good optics help the camera capture clear, sharp images for better inspection and data analysis.
Machine vision systems continue to evolve. High-speed, high-resolution cameras, advanced sensors, and smart data analysis tools make automated inspection more powerful and reliable than ever before.
Types of Industrial Cameras

Area Scan
Area scan cameras, also known as matrix cameras, capture entire 2D images at once using a sensor array. This image acquisition method makes them simpler and less technically demanding than line scan cameras. Area scan cameras work best for static scenes and objects. They are widely used in machine vision because they can capture full images instantly.
- Capture full 2D images in one shot
- Simpler setup compared to line scan cameras
- Ideal for barcode scanning, flaw detection, and measurement tasks
| Industrial Applications | Industries |
|---|---|
| Barcode Scanning | Automotive Manufacturing |
| Flat Panel Display Inspection | Electronics Inspection |
| Flaw Detection | Food & Packaging |
| Identification | Postal |
| In-line 3D Metrology | Manufacturing |
Line Scan
Line scan cameras capture images one line at a time as objects move past the sensor. This method allows continuous inspection of materials like textiles, paper, and metal sheets. Line scan cameras deliver extremely high resolution, uniform illumination, and fast image capture. They excel in machine vision for inspecting wide or fast-moving materials.
- Achieve high resolution, limited only by movement precision
- Provide consistent, distortion-free images
- Synchronize with object movement to prevent motion blur
- Reduce redundant data for efficient processing
3D and Embedded
3D cameras add depth information to machine vision, enabling precise automation and quality control. They help robots navigate and inspect complex surfaces. Embedded vision systems combine compact computing power with local image processing, reducing latency and cloud dependency. These systems use AI to sort products and detect defects in real time.
- Capture depth for accurate measurement and robotic guidance
- Improve productivity and reduce costs
- Enable real-time inspections and predictive maintenance
Industrial Smart Cameras
Smart cameras combine image capture and processing in a single, compact unit. They are cost-effective and easy to set up, with built-in lenses, lighting, and software. Smart cameras perform tasks like barcode reading, defect detection, and pattern matching. Their all-in-one design fits well into distributed control systems and small spaces.
- Fewer cables and components simplify installation
- Reliable in changing industrial environments
- User-friendly software requires no machine vision expertise
- Perform image processing on the edge, sending only results to central systems
| Interface | Data Transfer Speed | Cable Length | Power Delivery | System Integration Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GigE Vision | 1–10 Gbps | Up to 100m | PoE | Scalable, flexible, uses standard Ethernet |
| USB3 Vision | Up to 10 Gbps | Few meters | No PoE | Easy integration, short range |
| CoaXPress | Up to 12.5 Gbps | Up to 100m | Power over cable | High bandwidth, needs frame grabber |
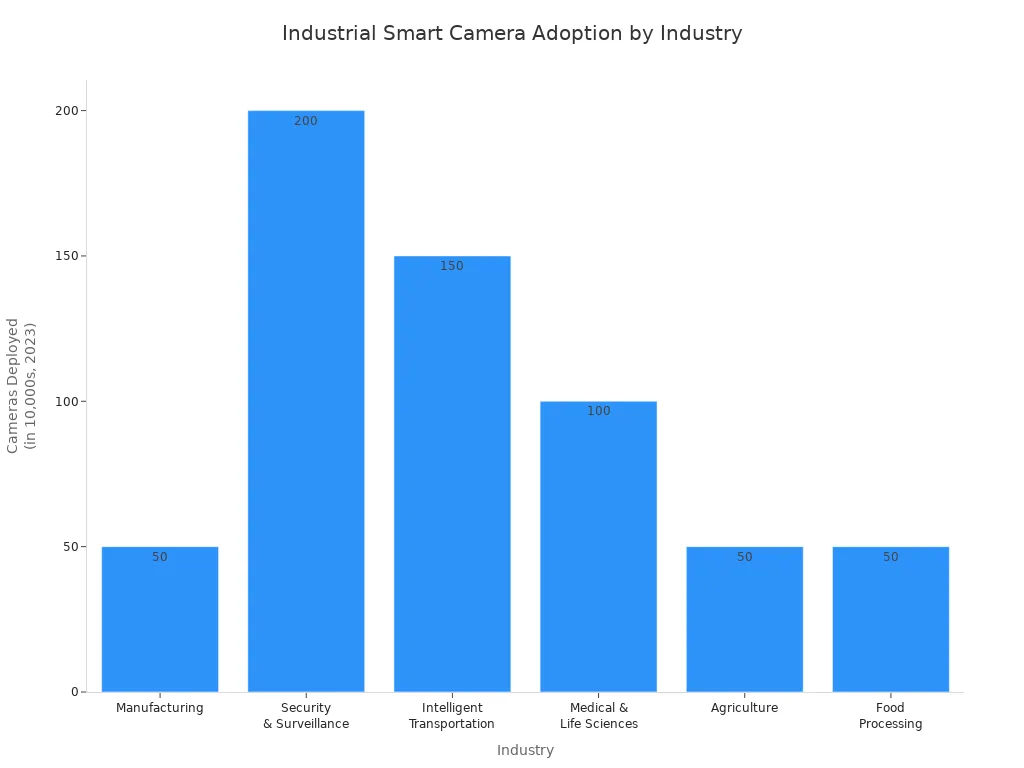
High-resolution cameras, advanced sensors, and fast interfaces like GigE and CoaXPress support demanding machine vision tasks. Smart cameras continue to transform industrial automation by making real-time inspections faster and more reliable.
Integration in Machine Vision
Lighting and Optics
Lighting and optics shape the foundation of every machine vision application. The right lighting setup improves image clarity, contrast, and reduces noise, which leads to better defect detection and measurement accuracy. Different lighting techniques—such as backlighting, ring lighting, coaxial lighting, and diffuse lighting—are chosen based on the surface of the object. For example, ring lighting works well for cylindrical parts, while darkfield lighting highlights scratches on reflective surfaces.
- Lighting and optics choices enhance the performance of smart cameras by:
- Improving image clarity and contrast
- Reducing noise for accurate industrial image processing
- Allowing control over depth of field and focus
Camera sensor sensitivity, spectral range, and shutter speed influence the intensity and type of lighting needed. High-sensitivity sensors may need less intense lighting, while fast shutter speeds require stronger illumination. Environmental factors like ambient light, temperature, and dust also affect lighting effectiveness. Shielding or using ambient light suppression technology helps maintain consistent results, especially in 3D machine vision.
Tip: Test and optimize lighting setups under different conditions to ensure robust and reliable industrial image processing.
Industrial Image Processing
Industrial image processing transforms raw images from smart cameras into valuable information. This process enables tasks such as defect detection, measurement, classification, and quality control. Advanced software tools automate complex visual tasks, reduce human error, and support real-time inspections. These tools include features like image filtering, color space conversion, segmentation, and classification.
| Category | Common Algorithms / Techniques |
|---|---|
| Contrast Enhancement | Histogram equalization, Adaptive histogram equalization |
| Feature Detection | Canny edge detector, SIFT, SURF, Hough transform |
| Segmentation | Region growing, Watershed transformation |
| Noise Removal Filters | Gaussian filter, Median filter |
| Other Techniques | Connected-component labeling, Seam carving |
Industrial image processing software, such as Cognex Vision Pro and MVTec Halcon, integrates with machine vision systems to synchronize image capture and processing. Open-source libraries like OpenCV and TensorFlow support AI and deep learning, enabling smart cameras to adapt to changing production needs. These solutions improve production quality and efficiency by providing fast, accurate, and scalable inspection.
System Communication
Smart cameras must communicate efficiently with other components in a machine vision system. Standard hardware interfaces like GigE Vision, USB3 Vision, and CoaXPress enable fast data transfer and camera control. Software layers such as GenICam ensure interoperability and easy access to camera features.
- Common communication protocols include:
- TCP/IP for data exchange over Ethernet
- DHCP for dynamic IP assignment
- Modbus for connecting to PLCs
- Precision Time Protocol for synchronizing multiple cameras
- PROFINET for fast industrial data exchange
High-speed machine vision applications face challenges like variable latency and the need for precise camera triggering. Direct sensor-to-camera wiring can reduce timing variability, improving reliability. Emerging standards such as CoaXPress and 10GigE support high data rates and long-distance transmission, making them ideal for real-time inspections and advanced industrial image processing.
Note: Reliable system communication ensures that smart cameras deliver accurate data analysis and support seamless automation in industrial environments.
Applications and Benefits

Quality Control
Industrial cameras machine vision system technology has transformed quality control in many industries. Manufacturers use machine vision cameras to inspect products at high speed and with great accuracy. These systems detect tiny defects, color changes, or assembly errors that human inspectors might miss. Real-time inspections allow immediate corrections, which improves production quality and reduces waste.
- Robotic guidance helps with precise assembly, increasing flexibility and accuracy.
- Automated pick-and-place operations sort and position parts, boosting throughput and lowering errors.
- Component verification systems check presence and orientation, preventing costly rework.
- Barcode and QR code reading systems track products, improving traceability.
- Hyperspectral imaging finds impurities invisible to the human eye, ensuring material quality.
Pharmaceutical companies like Bausch + Ströbel use high-speed cameras to monitor ampoule filling lines, catching underfilling or breakage at rates up to 1,000 items per minute. Battery makers such as Varta use slow-motion video to spot missing electrolyte drops, reducing contamination and downtime. These examples show how industrial applications benefit from advanced optical inspection and industrial image processing.
Automation
Machine vision systems drive automation across manufacturing, medical imaging, and life sciences. Industrial smart cameras process high-resolution images in real time, guiding robots and checking dimensions. AI and machine learning improve anomaly detection and decision-making, making production lines smarter over time.
- Real-time monitoring reduces downtime by catching issues early.
- Integration with ERP, MES, and robotics creates seamless workflows.
- Automated inspections keep workers safe by handling hazardous tasks.
- Data analysis from camera systems helps optimize production and supports predictive maintenance.
In medical imaging, industrial cameras with enhanced sensitivity support cancer diagnostics and personalized treatment. Portable devices with smart cameras enable remote diagnostics and telehealth, expanding healthcare access. Life sciences use high-resolution cameras for digital pathology, cell biology, and in-vitro diagnostics, where fast and accurate image acquisition is critical.
Speed and Cost Savings
Industrial applications see major gains in speed and cost savings with machine vision systems. Automated inspection can check hundreds or thousands of products per minute without losing quality. Real-time defect detection allows immediate action, reducing waste and improving consistency.
| Metric | Improvement / Reduction |
|---|---|
| Assembly line accuracy | 25% increase |
| Efficiency gains in robotics | Up to 40% |
| Defect rate reduction | Up to 30% |
| Production downtime reduction | 35% decrease |
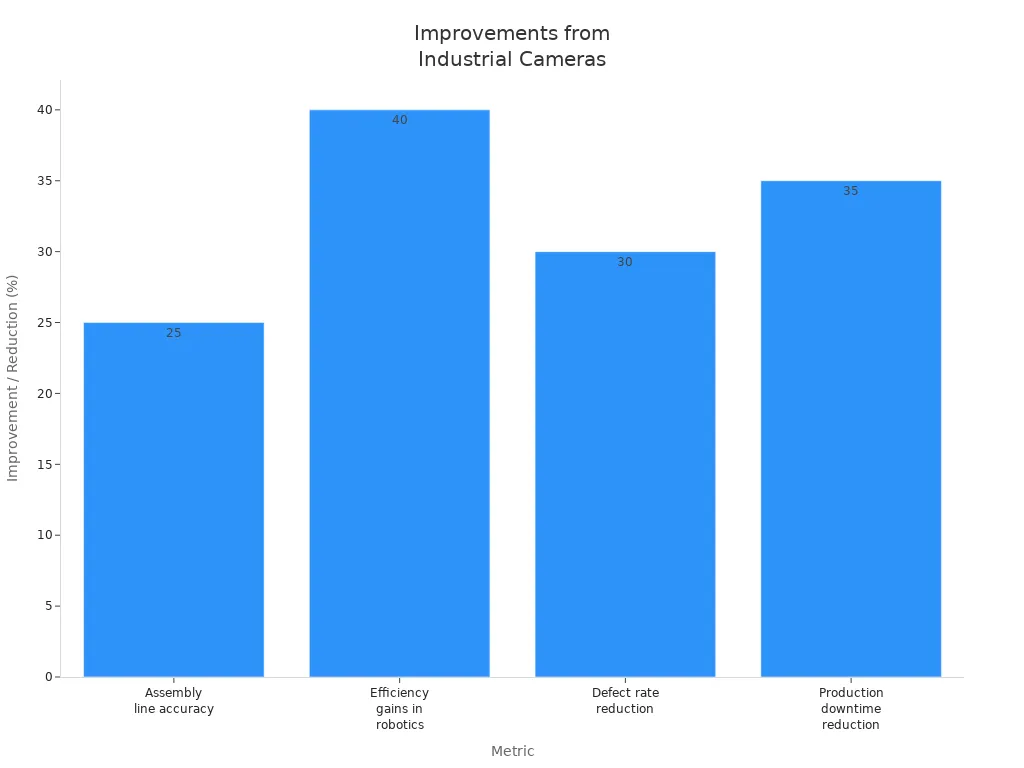
Manufacturers report up to a 30% reduction in waste and a 25% drop in downtime. Automated inspections lower labor costs and minimize defective products, leading to better return on investment. The use of MIPI A-PHY interfaces in embedded vision systems also cuts hardware and maintenance costs. As production scales, comprehensive monitoring and calibration keep results consistent, even at high speeds.
Industrial cameras machine vision system technology delivers faster, more reliable, and cost-effective production for a wide range of industrial applications.
Industrial cameras machine vision system technology drives modern automation by enabling precise inspection, fast image acquisition, and reliable data analysis. Machine vision cameras, including industrial smart cameras, support real-time inspections and improve production quality across many industrial applications. Selecting the right camera systems involves considering factors like resolution, lighting, and environmental needs. The table below highlights key considerations for optimal camera selection:
| Consideration | Importance |
|---|---|
| Resolution | Detects small defects and features |
| Lighting | Ensures clear optical inspection |
| Integration | Matches image processing and software needs |
| Durability | Handles harsh industrial environments |
Staying updated with high-resolution cameras and advanced industrial image processing helps industries achieve better results and long-term success.
FAQ
What is the main role of industrial cameras in machine vision systems?
Industrial cameras help machines see and understand objects. They capture images for inspection, measurement, and sorting. These cameras support machine vision systems in many industrial applications, improving production quality and reducing errors.
How do smart cameras differ from traditional camera systems?
Smart cameras combine image acquisition and image processing in one device. They perform real-time inspections and data analysis without needing a separate computer. This makes them easy to use in many machine vision applications.
Why is lighting important in industrial image processing?
Proper lighting helps cameras capture clear images. Good lighting improves optical inspection and defect detection. It also supports high-resolution cameras in finding small flaws, which increases production quality and accuracy in machine vision systems.
Can machine vision cameras work in harsh industrial environments?
Yes. Many camera systems have rugged designs. They resist dust, heat, and vibration. This allows machine vision cameras and industrial smart cameras to perform reliable inspections in tough industrial settings.
What benefits do real-time inspections offer in production?
Real-time inspections catch defects quickly. They help fix problems before products leave the factory. This reduces waste, saves money, and keeps production running smoothly. Real-time data analysis also supports better decision-making in industrial applications.
See Also
Understanding The Role Of Cameras In Machine Vision
A Detailed Look At Electronics In Machine Vision
Why Proper Lighting Is Essential For Machine Vision Systems
Complete Guide To Machine Vision In Industrial Automation
Comparing Firmware-Based Machine Vision With Traditional Systems








